Step 1: Understand what immunoprecipitation is? Why should I do
immunoprecipitation?
Immunoprecipitation (IP) is a method for purifying and enriching target proteins from specific mixtures (usually cell lysates or expression supernatants) by using antigen-antibody specific reactions. The traditional IP experiment is that after the antibody is combined with the target protein, it is incubated with agarose or magnetic beads coupled with Protein A /G (Fc fragment of binding antibody), and the bead-protein A/G- antibody-target protein complex is obtained by centrifugation. The complex is washed and eluted for subsequent downstream experiments. IP is an important step in many protein-related researches. It is used to study the existence, relative abundance, up-down regulation of protein expression, protein-to-stability and interaction of proteins.
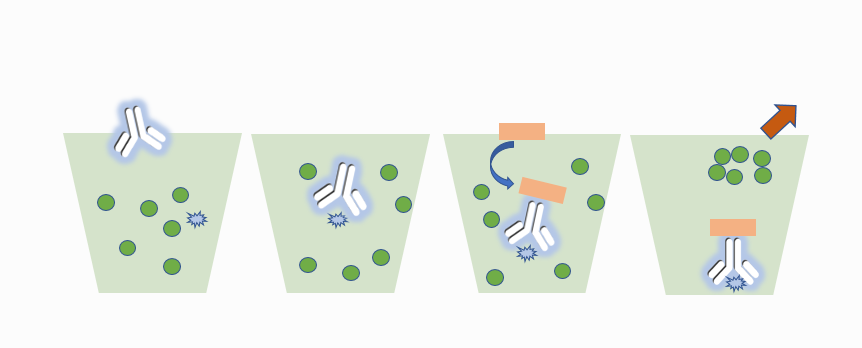
Summary: The key tools I need to use in the whole
process of IP are,
1) primary antibody: select the primary antibody that can
react with the sample and do IP experiment;
2) Potein A,Potein G or Protein
A /G:Potein A, Potein
G and Protein A /G have different binding abilities to immunoglobulins from
different sources and subtypes. how to choose? Please refer to https://www.abbkine.com/affinity-of-protein-a-protein-g-and-protein-ag/
3) Selection Guide:
Cat# | Product name |
BMR20500 | PurKine™ Protein A Resin |
BMR20504 | PurKine™ Protein A Resin 4FF |
BMR20600 | PurKine™ Protein G Resin |
BMR20604 | PurKine™ Protein G Resin 4FF |
BMR20704 | PurKine™ Protein A/G Resin 4FF |
Step 2: Finding that there is no suitable primary antibody to meet the immunoprecipitation I need to do?
Some target proteins cannot be immunoprecipitated because there is no
corresponding specific antibody. For example, the antigen epitope recognized by
the antibody is shielded by the interaction protein, unable to interact with
the target protein or the antibody selection is inappropriate, the selected
antibody cannot recognize the protein in natural conformation, etc. After an
epitope tag protein is used, the tag antibody against this epitope can be
selected for immunoprecipitation. Manufacturers will introduce some common
label antibodies for IP experiments, involving labels such as flag, HA, His and
Myc to meet the needs of most customers.
In particular, the agarose/magnetic bead coupled labeled antibody can
optimize the immunoprecipitation experiment to the greatest extent and save
time and cost.
1) Principle: The step of Protein A/G binding with antigen-antibody complex is omitted, and the problem of weak binding ability between Protein A/G and antibody is solved. After the conjugated antibody is directly combined with the target protein, the target protein is separated from the cell lysate by centrifugation or using a magnetic rack. The high-specificity monoclonal label antibody can realize high yield and high purity, and the stable and pre-sealed filler and the specific antibody reduce non-specific binding in the immunoprecipitation process.
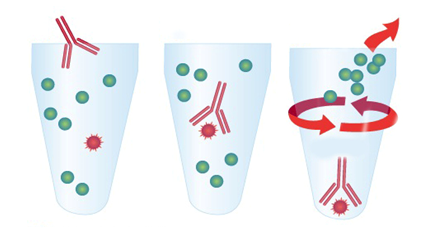
2) Selection Guide:
Cat# | Product name |
A02010AGB | Anti-DDDDK Tag Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (1B10), Agarose |
A02010MGB | Anti-DDDDK Tag Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (1B10), Magnetic Beads |
A02040AGB | Anti-HA Tag Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (4F6), Agarose |
A02040MGB | Anti-HA Tag Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (4F6), Magnetic Beads |
A02050AGB | Anti-His Tag Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (5C3), Agarose |
A02050MGB | Anti-His Tag Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (5C3), Magnetic Beads |
A02060AGB | Anti-Myc Tag Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (2D5), Agarose |
A02060MGB | Anti-Myc Tag Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (2D5), Magnetic Beads |
Step 3: How to deal with heavy chain and light chain interference in WB (IP-WB) after immunoprecipitation?
In WB verification after immunoprecipitation experiment, when
conventional Anti-IgG (H+L) enzyme labeled secondary antibody is used, two
bands corresponding to heavy chain (50kDa) and light chain (25kDa) generated
after denaturation of immunoprecipitation primary antibody will usually appear.
If the molecular weight of the detected target protein is near here, it will be
interfered by the two bands. How to avoid interference,
Method 1: Select the secondary antibody that only
reacts with heavy chain or light chain. If the molecular weight of the target
protein is less than 30KD, in order to avoid interference of antibody light
chain, heavy chain specific secondary antibody is selected; If the molecular
weight of the target protein is more than 30KD, in order to avoid interference
of antibody heavy chain, light chain specific secondary antibody is selected;
Selection Guide:
Cat# | Product name | Description |
A25012 | IPKine™ HRP, Goat Anti-Mouse IgG LCS | light chain specific |
A25022 | IPKine™ HRP, Mouse Anti-Rabbit IgG LCS | light chain specific |
A25112 | IPKine™ HRP, Goat Anti-Mouse IgG HCS | Heavy chain specific |
A25222 | IPKine™ HRP, Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG HCS | Heavy chain specific |
Method 2: When selecting WB primary antibody, select different species from IP primary antibody to avoid interference from IP primary antibody;
Method 3: Select the WB primary antibody directly coupled with HRP, and omit the
step of secondary antibody. Immune
precipitation is broken in three steps.
If you have any questions, welcome to contact
us.
没有评论:
发表评论